Noscapine ((S,R)-Noscapine)

(Synonyms: 那可汀) 目录号 : GC32821
Noscapine是一种口服止咳药,主要通过其σ受体激动剂活性调节,且Noscapine具有抗癌活性。
Cas No.:128-62-1
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Noscapine is an orally administrable drug used worldwide for cough suppression, primarily mediated by its σ-receptor agonist activity, and possess anticancer activity.Target: σ-receptorin vitro: Noscapine is a phthalideisoquinoline alkaloid from opium, is a recently discovered anticancer drug and is currently under investigation in phase-I/II clinical trials for the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma. Noscapine causes few or no side effects and has been widely used as a cough suppressant in developing countries. Noscapine has been demonstrated to interact with microtubules. Interestingly, unlike many other microtubule-targeting agents such as Paclitaxel and Nocodazole, Noscapine does not obviously affect the total amount of microtubule polymers in cells; instead, it significantly increases the time microtubules spend in the pause state. The alteration of microtubule dynamics then activates the spindle checkpoint and arrests cell cycle progression at mitosis, leading to apoptotic cell death.
[1]. Yang Y, et al. CYLD Regulates Noscapine Activity in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia via a Microtubule-Dependent Mechanism. Theranostics. 2015 Mar 2;5(7):656-666.
| Cas No. | 128-62-1 | SDF | |
| 别名 | 那可汀 | ||
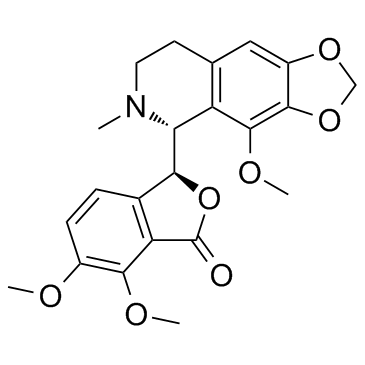
| Canonical SMILES | O=C1O[C@H]([C@@H]2N(C)CCC3=C2C(OC)=C(OCO4)C4=C3)C5=C1C(OC)=C(OC)C=C5 | ||
| 分子式 | C22H23NO7 | 分子量 | 413.42 |
| 溶解度 | DMSO : ≥ 30 mg/mL (72.57 mM) | 储存条件 | Store at -20°C |
| General tips | 请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 储备液的保存方式和期限:-80°C 储存时,请在 6 个月内使用,-20°C 储存时,请在 1 个月内使用。 为了提高溶解度,请将管子加热至37℃,然后在超声波浴中震荡一段时间。 |
||
| Shipping Condition | 评估样品解决方案:配备蓝冰进行发货。所有其他可用尺寸:配备RT,或根据请求配备蓝冰。 | ||
| 制备储备液 | |||
 |
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 2.4188 mL | 12.0942 mL | 24.1885 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4838 mL | 2.4188 mL | 4.8377 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2419 mL | 1.2094 mL | 2.4188 mL |
| 第一步:请输入基本实验信息(考虑到实验过程中的损耗,建议多配一只动物的药量) | ||||||||||
| 给药剂量 | mg/kg |  |
动物平均体重 | g |  |
每只动物给药体积 | ul |  |
动物数量 | 只 |
| 第二步:请输入动物体内配方组成(配方适用于不溶于水的药物;不同批次药物配方比例不同,请联系GLPBIO为您提供正确的澄清溶液配方) | ||||||||||
| % DMSO % % Tween 80 % saline | ||||||||||
| 计算重置 | ||||||||||
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/ml;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL,
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL saline,混匀澄清。
1. 首先保证母液是澄清的;
2.
一定要按照顺序依次将溶剂加入,进行下一步操作之前必须保证上一步操作得到的是澄清的溶液,可采用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等物理方法助溶。
3. 以上所有助溶剂都可在 GlpBio 网站选购。
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet





















