RY796

目录号 : GC64691
RY796 是一种有效的选择性电压门控钾 (KV2) 通道抑制剂,对 KV2.1 和 KV2.2 的 IC50 值分别为 0.25 μM 和 0.09 μM。RY796 可用于缓解疼痛的研究。
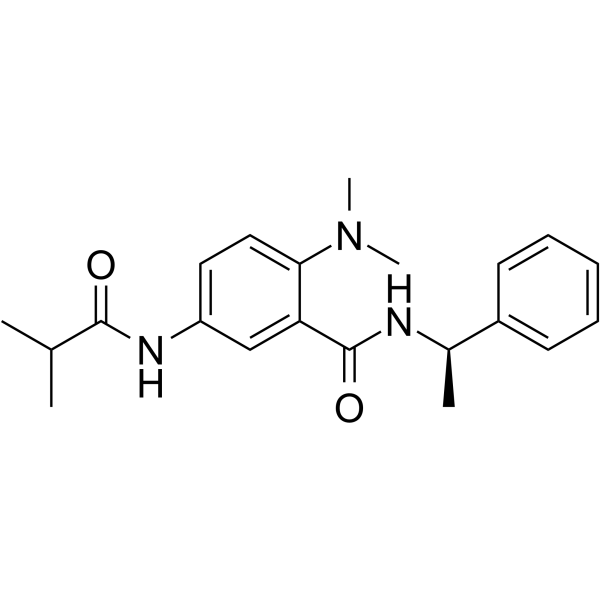
Cas No.:1393441-53-6
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
RY796 is a potent and selective voltage-gated potassium (KV2) channel inhibitor with IC50s of 0.25 μM and 0.09 μM for KV2.1 and KV2.2. RY796 has analgesic activity[1].
[1]. Herrington J, et al. Identification of novel and selective Kv2 channel inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Dec;80(6):959-64.
| Cas No. | 1393441-53-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| 分子式 | C21H27N3O2 | 分子量 | 353.46 |
| 溶解度 | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (282.92 mM; Need ultrasonic) | 储存条件 | Store at -20°C |
| General tips | 请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 储备液的保存方式和期限:-80°C 储存时,请在 6 个月内使用,-20°C 储存时,请在 1 个月内使用。 为了提高溶解度,请将管子加热至37℃,然后在超声波浴中震荡一段时间。 |
||
| Shipping Condition | 评估样品解决方案:配备蓝冰进行发货。所有其他可用尺寸:配备RT,或根据请求配备蓝冰。 | ||
| 制备储备液 | |||
 |
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 2.8292 mL | 14.1459 mL | 28.2917 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5658 mL | 2.8292 mL | 5.6583 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2829 mL | 1.4146 mL | 2.8292 mL |
| 第一步:请输入基本实验信息(考虑到实验过程中的损耗,建议多配一只动物的药量) | ||||||||||
| 给药剂量 | mg/kg |  |
动物平均体重 | g |  |
每只动物给药体积 | ul |  |
动物数量 | 只 |
| 第二步:请输入动物体内配方组成(配方适用于不溶于水的药物;不同批次药物配方比例不同,请联系GLPBIO为您提供正确的澄清溶液配方) | ||||||||||
| % DMSO % % Tween 80 % saline | ||||||||||
| 计算重置 | ||||||||||
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/ml;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL,
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL saline,混匀澄清。
1. 首先保证母液是澄清的;
2.
一定要按照顺序依次将溶剂加入,进行下一步操作之前必须保证上一步操作得到的是澄清的溶液,可采用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等物理方法助溶。
3. 以上所有助溶剂都可在 GlpBio 网站选购。
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet





















